
If intravascular fluid loss is severe, the body cannot maintain adequate blood pressure and perfusion of vital organs. Intravascular fluidloss can be caused by several factors, such as excessive diuretic use, severe bleeding, vomiting, diarrhea, and inadequate oral fluid intake.
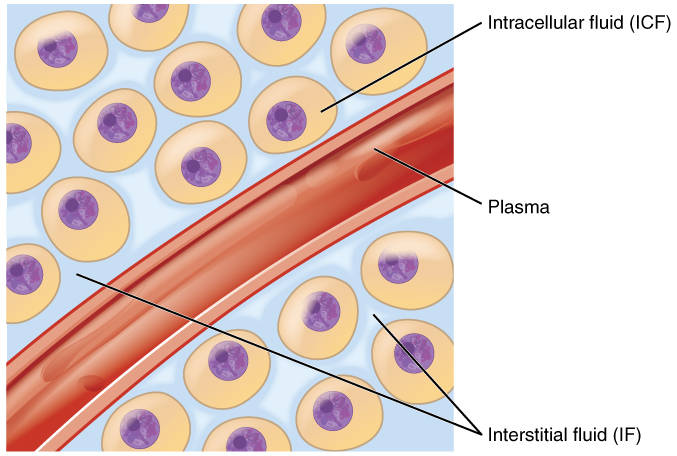
Loss of intravascular fluids causes the nursing diagnosis Deficient Fluid Volume, also referred to as hypovolemia. Intravascular fluid is the most important component of the body’s overall fluid balance. Intravascular fluid is whole blood volume and also includes red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma, and platelets. The first type is known as intravascular fluid that is found in the vascular system that consists of arteries, veins, and capillary networks. The body regulates sodium levels to control the movement of water into and out of the extracellular space due to osmosis.Įxtracellular fluids can be further broken down into various types. The most abundant electrolyte in extracellular fluid is sodium. In fact, intracellular fluid accounts for 60% of the volume of body fluids and 40% of a person’s total body weight! Įxtracellular fluids (ECF) are fluids found outside of cells. Intracellular fluids are crucial to the body’s functioning. The most abundant electrolyte in intracellular fluid is potassium. Intracellular fluids (ICF) are found inside cells and are made up of protein, water, electrolytes, and solutes. Figure 15.1 Intracellular and Extracellular Compartments See Figure 15.1 for an illustration of intracellular and extracellular compartments. Body fluids are found in two main areas of the body called intracellular and extracellular compartments. \)īody fluids consist of water, electrolytes, blood plasma and component cells, proteins, and other soluble particles called solutes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
